slide chương 5-
Tên môn học: Thống kê trong kinh doanh
Giá: 0đ
0đ
Chi tiết
tài liệu :
| Định dạng | |
| Dung lượng | 1.15 MB |
| Số trang | 33 |
| Ngành | Quản lý công nghiệp |
| Ngày đăng | 02/09/2025 |
| Lượt xem | 7 |
| Lượt bán | 0 |
C5
Chapter 5
Decision Analysis
Problem Formulation
Decision making with probabilities
Decision analysis with sample information
Computing branch probabilities using Bayes’ theorem
1
Problem Formulation
Bước đầu tiên trong quy trình decision analysis là
problem formulat...
Decision Analysis
Problem Formulation
Decision making with probabilities
Decision analysis with sample information
Computing branch probabilities using Bayes’ theorem
1
Problem Formulation
Bước đầu tiên trong quy trình decision analysis là
problem formulat...
Một số trang tài liệu:

Trang 1

Trang 8
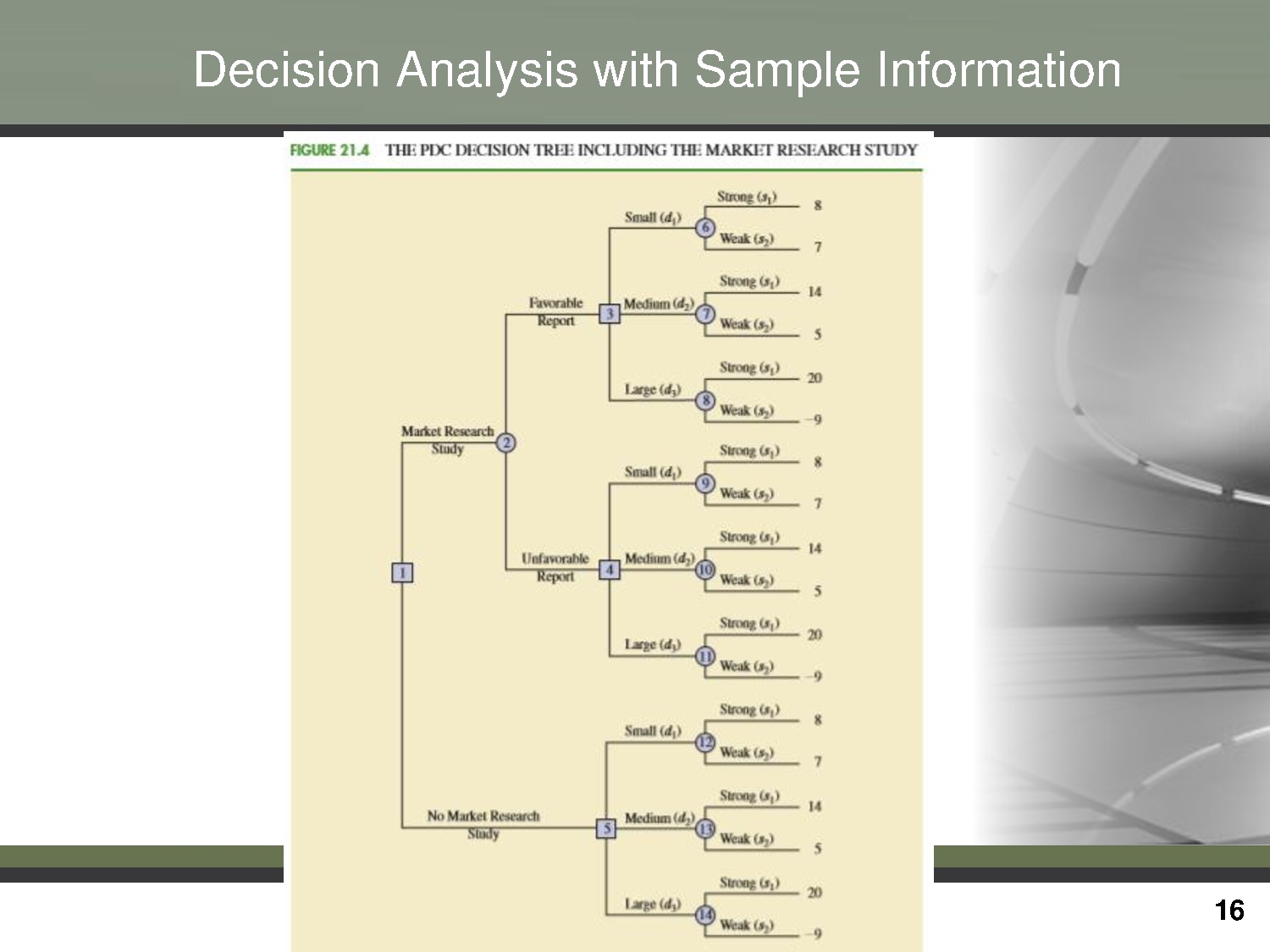
Trang 16
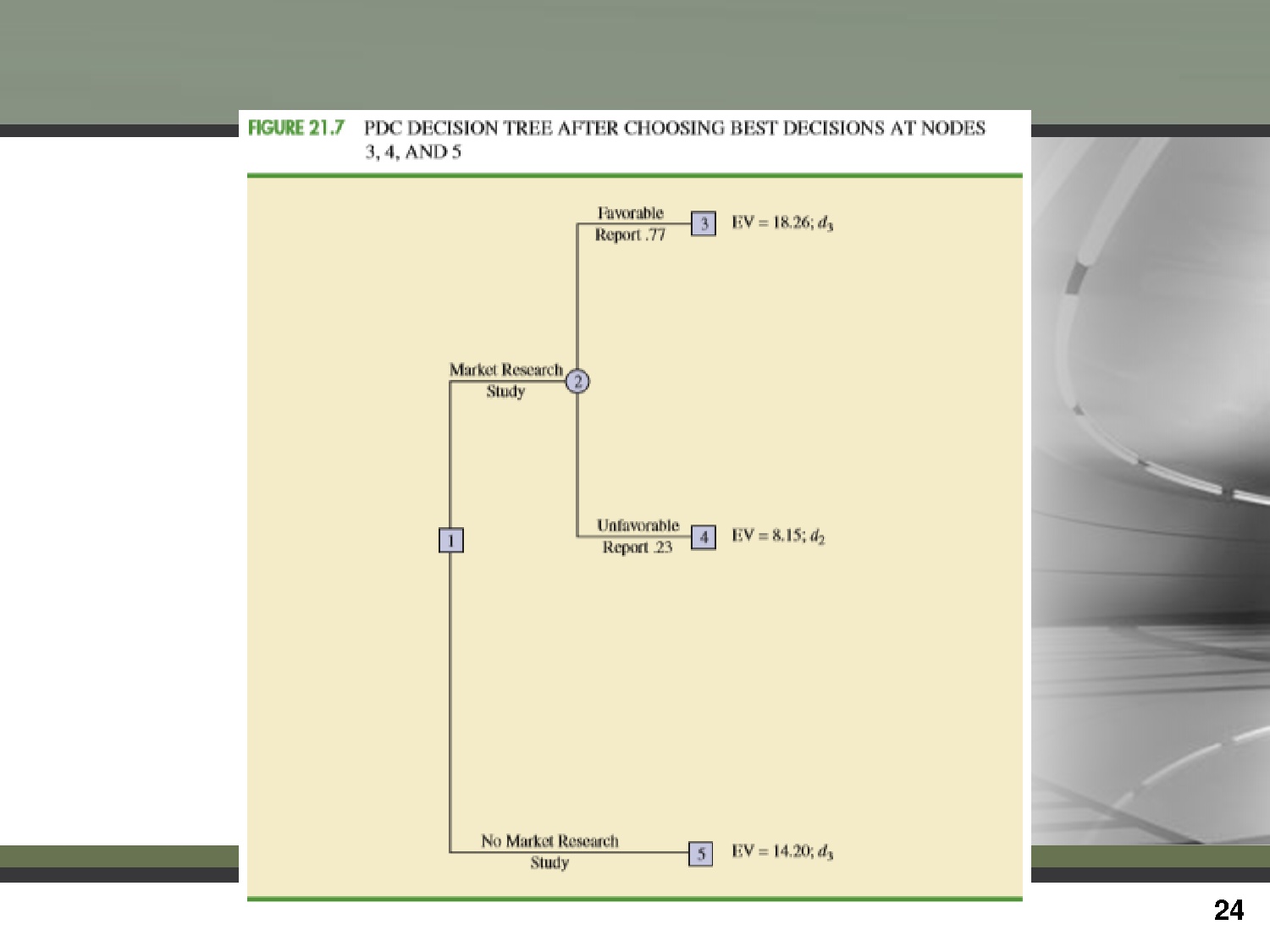
Trang 24
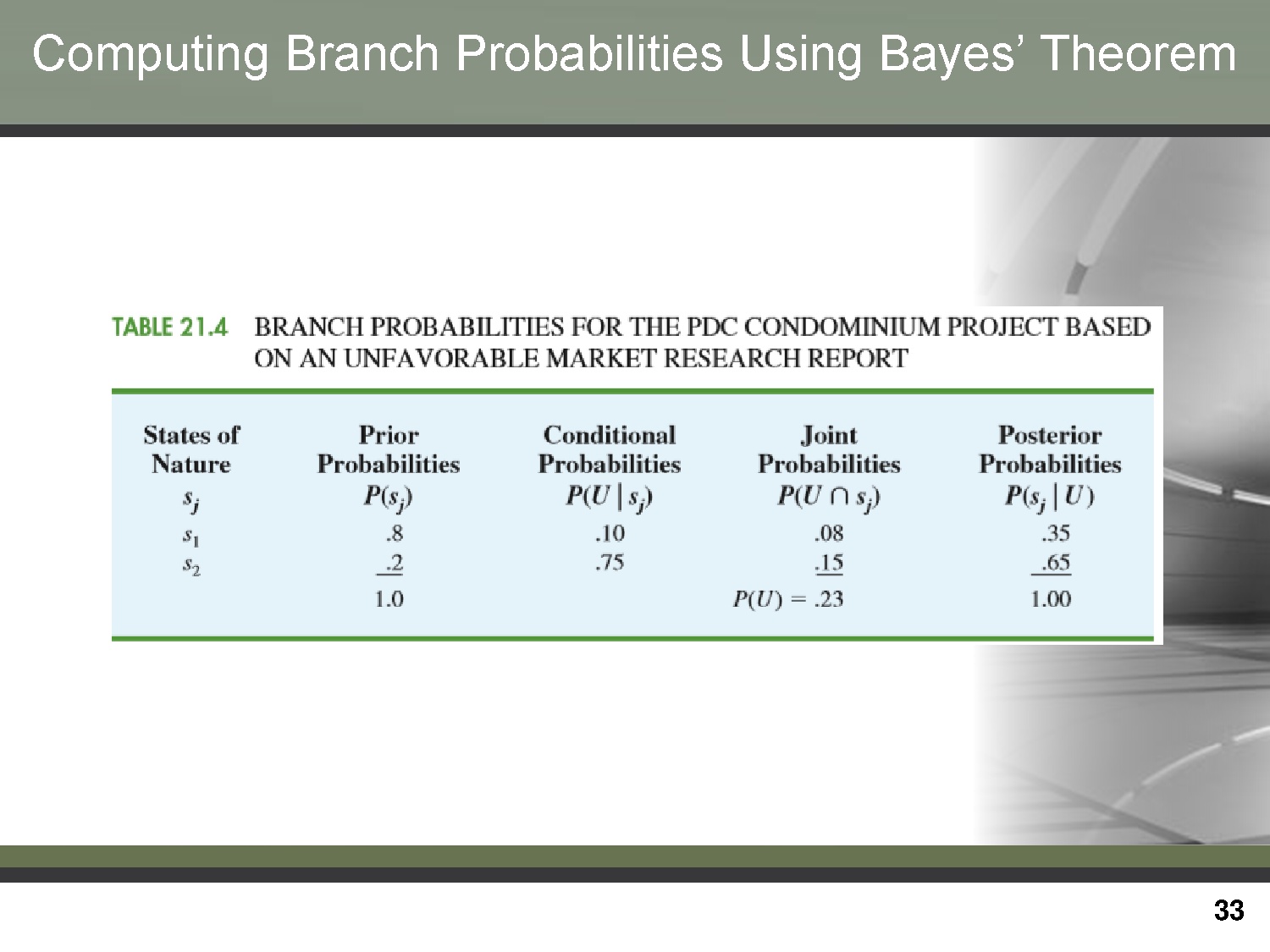
Trang 33